HDR, short for High Dynamic Range, represents an exciting advance in TV picture quality. HDR expands a TV’s brightness range, color palette, and contrast ratio to deliver images that look far more realistic to the human eye.
Introduced in 2015, HDR has quickly become a must-have feature for 4K Ultra HD televisions. It takes the viewing experience to new immersive heights by making imagery on the screen truly come alive with incredible nuance and depth.
This article will provide an in-depth look at HDR technology – what it means, how it works, the visual benefits it offers, the different HDR formats, content availability, and tips for buying an HDR TV.
We’ll also answer some frequently asked questions to help demystify HDR terminology and shed light on how it provides a revolutionary leap in home entertainment.

What is HDR?
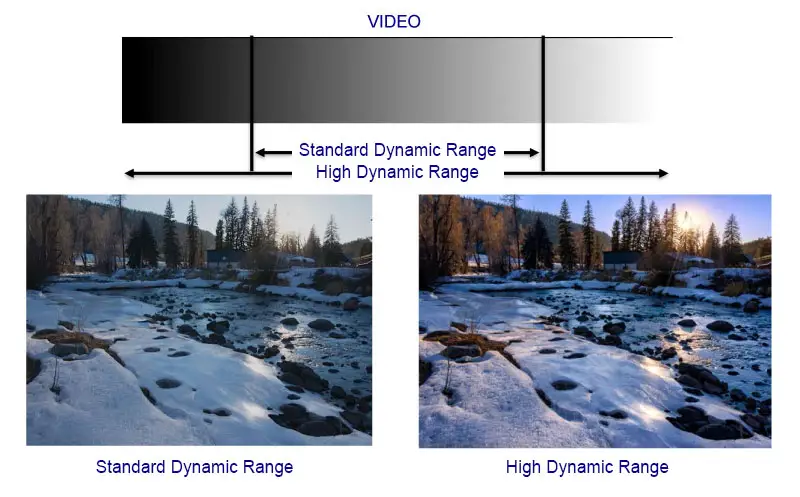
HDR stands for High Dynamic Range. It is an imaging technology that significantly expands a display’s visual dynamic range, which is the difference between the brightest whites and the deepest blacks a TV can produce.
HDR builds upon the color and resolution benefits of 4K Ultra HD. While 4K increases pixel count for sharpness and clarity, HDR enhances pixel quality by augmenting brightness, color, and contrast.
The result is ultra-realistic images with finer detail and texture than previously possible with standard HD or 4K alone.
In technical terms, HDR increases the luminosity range from 0 to 10,000 nits (a measure of brightness), compared to about 100 nits on conventional displays.
This immense range allows for truly vibrant, dazzling highlights while still maintaining deep inky blacks. HDR also delivers a more expanded color gamut, revealing subtle shades that get lost on non-HDR displays.
How HDR Works
HDR-compatible TVs contain advanced panels with special backlighting technology, optimized LED dimming zones, and 10 or 12-bit color depth capable of displaying billions of colors.
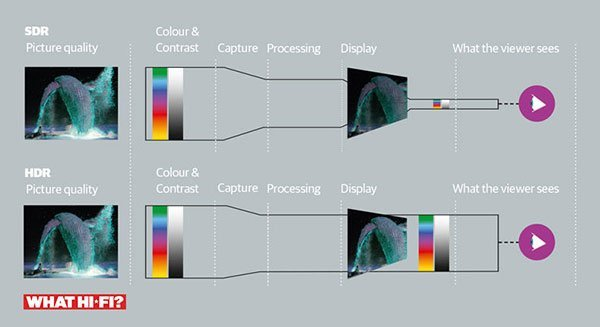
HDR content contains scene-by-scene metadata that instructs the TV how to render brightness, contrast, and color for each frame.
The TV’s video processor uses dynamic tone mapping to map video from the HDR format’s expanded color space into the display’s native color gamut.
To fully realize the advantages, the TV must be capable of reaching high nits levels. That’s why high peak brightness and local dimming zones are key features of HDR-enabled sets.
At the pixel level, HDR brings out fine details in both shadows and highlights that lend images a true-to-life look.
Benefits of HDR
Here are some of the key benefits HDR delivers:
- Brighter, more vibrant, and richer colors
- Much greater contrast ratio between blacks and peak whites
- Enhanced depth, dimensionality, and image texture
- Reveals subtle details that get lost in standard video
- More lifelike specular highlights like sunlight glint and reflections
- Accurately render real-world color, brightness, and contrast
- Closer to what the human eye sees in the natural world
- An immersive visual experience that simulates 3D depth
In summary, HDR makes what you watch look more real, visually engaging, and true to the creator’s intent. It unlocks a wider spectrum of light and color for breathtaking picture quality.
HDR Formats
There are several HDR formats used in TVs today. Key ones include:
- HDR10 – The most widely adopted HDR standard. Uses open, royalty-free technology.
- Dolby Vision – Advanced proprietary format mastered for scene-by-scene color and dynamic range.
- HLG (Hybrid Log Gamma) – Optimized for broadcasting live HDR content over cable/satellite networks.
- HDR10+ – Enhancement to HDR10 adds dynamic metadata for optimized scene-by-scene performance.
- Advanced HDR by Technicolor – Integrates artistic color science into dynamic tone mapping.
Most premium 4K TVs today support multiple HDR formats via firmware updates. Top streaming devices like Apple TV 4K also support various HDR technologies.
HDR Content
To enjoy HDR’s dazzling visuals, you need access to HDR-encoded movies, shows, and games. Major sources include:
- Ultra HD Blu-ray – Offers best-in-class HDR picture quality. Disks are encoded with HDR10 and Dolby Vision.
- Streaming – Netflix, Amazon, Disney+, and Apple TV+ offer a growing library of HDR titles. Needs fast broadband speeds.
- Gaming – Xbox One S/X, PS4, and PS5 output games in HDR. Heightened realism and detail.
- Live TV – Pay TV providers like Dish, DirecTV, and Comcast now broadcast some channels and events in HDR.
While HDR content is increasing, most existing video maxes out at the standard dynamic range. But many 4K TVs can upscale SDR to simulate HDR effects.
Buying an HDR TV – Key Factors to Consider
If you want to experience HDR’s stunning visuals, here are some key TV features to look for:
- High peak brightness – Needs brightness over 500-1000 nits for impactful HDR highlights. OLED and full-array local dimming achieve this well.
- Wide color gamut – Look for at least 90% DCI-P3 coverage for richer, more detailed color reproduction. Quantum dot technology excels here.
- Multiple HDR formats – Top TVs support various HDR technologies like HDR10, Dolby Vision, and HLG via firmware updates.
- HDMI connectivity – Needs HDMI 2.0a/HDCP 2.2 ports to handle HDR content from external devices.
- Processor – The TV’s video processor must handle HDR’s expanded brightness/color and convert it to the screen’s native capabilities.
- Content library – Ensure your favorite streaming apps and external devices offer a good selection of HDR programming.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Is HDR the same thing as 4K resolution?
Ans: No, HDR and 4K are complementary technologies. 4K refers to display resolution, while HDR improves brightness, color depth, and contrast. Most 4K TVs today also support HDR. But you can have 4K without HDR or HDR on a 1080p screen.
Q2: Do I need an HDR TV to enjoy HDR content?
Ans: To fully experience the visual benefits like enhanced color and contrast, an HDR-capable TV is required. Many 4K TVs now support HDR. Streaming devices and discs also need to output HDR content to an HDR TV.
Q3: Does HDR make a difference on smaller screens?
Ans: HDR’s advantages may be subtler on smaller screens. Larger screen sizes above 55 inches will be most impactful for HDR to reveal finer detail and texture. But HDR can still improve picture quality even on smaller 4K sets.
Q4: Is nits the same as brightness?
Ans: Yes, nits and brightness are essentially the same. Nits are a measure of luminance intensity. TVs with higher nit/brightness levels can achieve a wider luminosity range and better HDR performance.
Q5: Do I need new HDMI cables for HDR?
Ans: HDMI cables must support HDMI 2.0a with HDCP 2.2 copy protection. Many existing Premium Certified HDMI cables will work, but some older cables may not handle HDR content. Using 18Gbps Ultra High-Speed HDMI cables is recommended.




